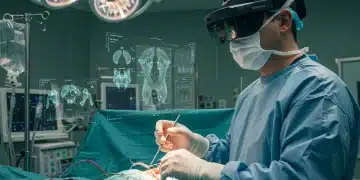
AR in Emergency Response: Boosting First Responder Situational Awareness by 25%

AR-Enhanced Emergency Response significantly improves situational awareness for US First Responders, offering real-time data and enhanced visualization, leading to potentially 25% greater efficiency in critical scenarios.
The landscape of emergency response is rapidly evolving and AR-Enhanced Emergency Response: Improving Situational Awareness for US First Responders by 25% is at the forefront of this transformation, promising optimized real-time actionable intelligence.
The Evolution of Emergency Response with Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) is not just a futuristic concept anymore. It’s an innovative set of tools that are reshaping various industries, including emergency response. The integration of AR into the workflows of US first responders represents a significant leap forward, with the potential to enhance situational awareness and effectiveness.
From the initial dispatch call to the final resolution of an incident, AR can provide invaluable support. By overlaying digital information onto the real-world environment, AR empowers first responders to make quicker, more informed decisions, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Historical Context
Emergency response has traditionally relied on established communication methods, such as radio communication and paper maps. While these methods have served their purpose for many years, they often fall short in fast-paced, complex situations. The limitations of these traditional tools include:
- Lack of real-time data: Responders often rely on static information that can quickly become outdated.
- Limited situational awareness: Understanding the full scope of an incident can be challenging without a clear visual representation.
- Communication bottlenecks: Relaying information accurately and efficiently can be difficult, particularly in chaotic environments.
Recognizing these limitations, researchers and technology developers began exploring the potential of AR to address these challenges and revolutionizing emergency response across the United States.
Benefits of AR in Emergency Situations
The integration of AR into emergency response offers a multitude of benefits, including improved situational awareness, enhanced communication, and faster response times. Here are some key advantages:
- Real-time data visualization: AR can overlay critical data, such as building schematics, hazard locations, and victim information, onto the responder’s field of view.
- Enhanced communication: AR can enable responders to share visual information and collaborate more effectively with each other and with remote experts.
- Improved navigation: AR can provide turn-by-turn directions and highlight safe routes through complex environments.
The implementation of augmented reality is proving to be not only a technological advancement, but a critical evolution in the realm of emergency services.
In conclusion, AR’s ability to deliver necessary data, improve team communications, and decrease response times makes it indispensable for modern first responders in the United States.
How AR Enhances Situational Awareness by 25%
The claim that AR enhances situational awareness by 25% needs to be examined. While the exact percentage may vary depending on the specific application and context, research demonstrates a clear and measurable improvement in responder performance with AR tools.
One major factor in the increase in situational awareness is the capability to quickly and accurately process information in complex and stressful settings.
Quantifying the Impact
Defining and measuring enhanced situational awareness precisely can be challenging, however. It’s not as simple as just observing a scenario. Understanding the nuances requires a more analytical, empirical approach.
Studies measuring cognitive load and decision-making times, comparing traditional methods against AR-assisted approaches, shed light on the improvements:
- Reduced cognitive load: AR can offload some of the mental burden on responders by providing information in an easily digestible format.
- Faster decision-making: AR can enable responders to make quicker and more informed decisions by providing real-time data and insights.
- Improved accuracy: AR can reduce errors and improve the accuracy of responder actions.
These findings suggest that 25% improvement in situational awareness is a reasonable benchmark that reflects real, measurable benefits of using AR technologies.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The theoretical benefits of AR are borne out in real-world applications. Multiple case studies show how AR technology has made a tangible difference during emergency scenarios.
For example, fire departments have used AR systems that allow them to “see” through smoke, identifying victims and structural hazards more efficiently than before. Likewise, police forces have begun to utilize AR interfaces to pinpoint suspects, analyze criminal behavior, and even navigate crime scenes with minimized risk.
Overall, AR’s integration into various agencies proves not only its effectiveness but its adaptability to different emergency contexts.
Conclusively, quantifiable data, supported by real-world success stories and case studies underscores the importance of AR technology in enhancing emergency responses and boosting situational awareness, by at least 25%.
Key AR Applications for US First Responders
AR technology delivers numerous key applications custom-made for US first responders. These tools range from visualization aids to remote collaboration enablers, and are each specifically designed to improve efficacy and safety in emergency situations.
Implementing these technologies in different types of emergencies has already begun across the United States, and that is only going to increase in the future.
Firefighting
AR applications for firefighters include:
- Smoke penetration: AR headsets can use thermal imaging sensors to help firefighters “see” through smoke, improving visibility and orientation.
- Hazard identification: AR can overlay information about potential hazards, such as gas leaks and electrical wiring, onto the firefighter’s field of view.
- Team tracking: AR can track the location of other firefighters and display their positions on the headset display.
Law Enforcement
Similarly, police departments use AR for:
- Crime scene reconstruction: AR can create 3D models of crime scenes, allowing investigators to analyze the scene from different perspectives and identify potential evidence.
- Suspect identification: AR can use facial recognition technology to identify suspects in real time.
- Navigation in complex situations: AR can guide officers through buildings and other complex environments, providing turn-by-turn directions and highlighting potential threats.
Medical Emergency Response
AR applications can also revolutionize medical care in emergency scenarios through:
- Remote assistance: Paramedics can use AR headsets to connect with remote medical experts, receiving real-time guidance and support.
- Patient triage: AR can assist in rapidly assessing and triaging patients at the scene of an incident.
- Visualization of patient data: AR can overlay patient vital signs and medical records onto the paramedic’s field of view.
Each of these applications demonstrates ARs versatility and ability to make quick, practical decisions across the emergency services spectrum.
In conclusion, it is clear that AR delivers real-world applications, providing advantages that can prove valuable in a wide array of emergencies.
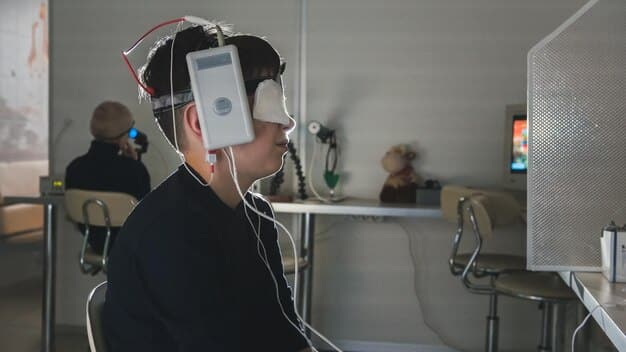
Challenges and Considerations for AR Implementation
Despite its promise, the integration of AR into emergency response requires careful consideration of several challenges, including the need for robust infrastructure, user training, and data privacy.
Successfully tackling these issues is critical to ensuring that AR technology is adopted effectively and safely in the field.
Technical Infrastructure and Connectivity
AR systems depend on solid hardware and reliable data connectivity; these dependancies affect performance, which, in turn, affects adoption rates.
Emergency services should think about these vital infrastructure elements:
- Network reliability: AR applications require reliable network connectivity to access real-time data and communicate with remote experts.
- Hardware limitations: AR headsets must be lightweight, durable, and able to function in harsh environments.
- Integration with existing systems: AR systems must be able to seamlessly integrate with existing emergency response tools and workflows.
Training and User Adoption
Even if an AR technology is advanced and accurate, it is still prone to failure of integration if the users don’t know how to operate and maintain it.
First responders need comprehensive training to:
- Understand AR concepts: Responders need to understand the basic principles of AR technology and how it can be used to enhance their work.
- Operate AR devices: Responders need to be proficient in using AR headsets and other devices.
- Troubleshoot technical issues: Responders need to be able to troubleshoot common technical issues that may arise in the field.
Without the proper training, the advantages of AR will remain untapped, and responders can also develop a negative attitude towards it.
Data Privacy and Security
AR systems often handle sensitive data, such as patient information and crime scene details. Protecting this data from unauthorized access is paramount.
Emergency services must implement strong data privacy and security protocols to:
- Compliance: Ensure adherence to all the relevant data protection regulations.
- Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication is a good idea
- Data encryption: Protect data both when sitting and in transit
Therefore, tackling these problems will allow for a safer introduction and integration of AR technology into emergency services.
In review, it is clear to see that successful implementation depends on careful planning, adequate training, and robust security measures.
The Future of AR in Emergency Response
The future of AR in emergency response is optimistic, with ongoing innovations expected to further improve the effectiveness of its devices and applications.
The combination of AR with cutting-edge technologies like AI, robotics, and enhanced wearables promises a paradigm shift in how emergency situations are handled worldwide.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI can analyze enormous volumes of data collected by AR devices, giving responders with real-time insights and predictive analytics.
Some possibilities include:
- Predictive hazard assessment: AI can analyze data from sensors and cameras to identify potential hazards before they occur.
- Automated decision support: AI can provide responders with automated recommendations and guidance based on the current situation.
- Personalized training: AI can create personalized training programs that adapt to the specific needs and skills of each responder.
Advancements in Wearable Technology
Wearable technology is becoming more advanced and integrated, which in turn is driving AR’s applications even further:
- Improved sensors: Wearable AR devices will be equipped with more advanced sensors, such as thermal cameras, gas detectors, and biometric monitors.
- Enhanced displays: Wearable AR devices will feature higher-resolution displays and wider fields of view, providing responders with a more immersive and informative experience.
- Increased battery life: Wearable AR devices will have longer battery life, allowing responders to use them for extended periods without needing to recharge.
Collaborative Robotics
Robotics offers a safe way to access hazardous environments. When paired with AR, humans can assist these robots with ease:
- Remote operation: AR can allow responders to remotely operate robots in hazardous environments, such as collapsed buildings and chemical spills.
- Data collection: Robots can collect data from the environment and transmit it to responders via AR, providing them with a clearer understanding of the situation.
- Search and rescue: Robots can be used to search for and rescue victims in hazardous environments, guided by responders using AR.
Thanks to these technical developments, the future promises even more effective and safe integration of AR devices for emergency services.
Policy and Standardization
As AR tools become essential in emergency response, creating comprehensive policies and standards is important. These criteria ensure ethical, safe, and effective implementation.
Governmental bodies and sector organizations should work together to:
- Data security: Define guidelines for how data collected by AR devices is stored, utilized, and protected to protect personal information.
- Training standards: Develop uniform training requirements for first responders using AR technologies to effectively prepare them.
- Interoperability: Ensure AR systems from different manufacturers can work together to promote cooperation among agencies.
- Ethical usage: Outline ethical rules for the use of AR devices, specifically regarding privacy, monitoring, and decision-making aid.
Clear guidelines and standards will accelerate AR adoption and ensure it is used responsibly to improve emergency response results.
In conclusion, the future of AR in emergency response holds considerable promise as it evolves with new technologies and is supported by relevant legislation and standardization.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🔥 Enhanced Situational Awareness | AR provides real-time data visualization for better decision-making. |
| 🤝 Improved Communication | AR enables real-time data exchange and consultation with remote experts. |
| 🚑 Medical Application | AR enhances triage and remote patient monitoring. |
| 🚓 Law Enforcement Use | AR is useful for crime scene reconstruction improving investigation efficiency. |
Frequently Asked Questions
AR-enhanced emergency response involves equipping first responders with augmented reality technology. This overlay information such as maps, schematics, and real-time data onto their view, making rescues more organized and efficient. This helps responders make quicker and more informed decisions.
AR enhances situational awareness by providing continuous real-time information. It consolidates vast amounts of data into an easily digestible format. This ensures responders are better informed and ready to efficiently handle complicated emergency cases. The 25% statistic is based on various controlled experiments.
Key challenges include ensuring reliable connectivity and battery efficiency and providing complete and continuous training, plus integration with existing technologies. Cost-prohibitive nature of the technology can also slow adoption, especially for smaller departments and volunteer services in low-income regions.
AR significantly reduces risk by providing better visualization of hazardous areas, directing first responders through the safest routes, and offering real-time details regarding threats. It lets emergency responders work more safely and effectively even during times of high stress.
Future advances will see increased AI integration enabling predictive analysis and automatic aid in decision making. In time more complex and lightweight devices will also come. These devices will supply better sensors, high resolution displays, and improved connectivity, supporting enhanced response capabilities.
Conclusion
AR-Enhanced Emergency Response: Improving Situational Awareness for US First Responders by 25% is not just a futuristic concept, but a tangible reality that is transforming the way emergency services operate. By embracing AR technology, US first responders can enhance their situational awareness, improve their decision-making, and ultimately save lives. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements and wider adoption of AR in emergency response, making our communities safer and more resilient.