AR for Product Design: Reduce Prototyping Costs 18% in 3 Months
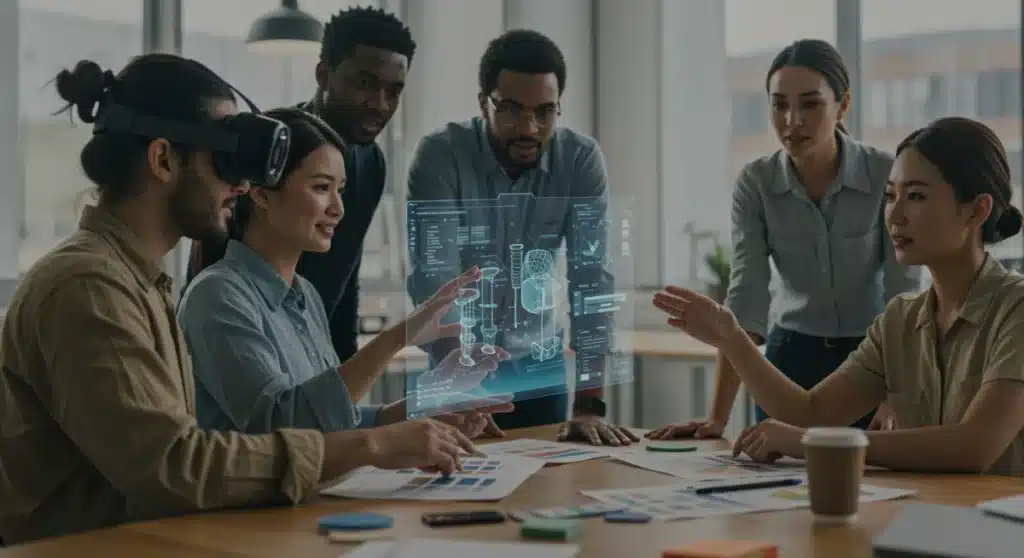

Leveraging augmented reality in product design offers US innovators a tangible opportunity to reduce prototyping costs by 18% within the next three months by streamlining iteration, improving visualization, and minimizing physical material waste.
Are you a US innovator looking to gain a significant edge in product development? The era of costly, time-consuming physical prototypes is rapidly evolving. Today, leveraging AR for product design: reducing prototyping costs by 18% for US innovators in the next 3 months is not just a futuristic concept but a quantifiable reality. Augmented reality is transforming how products are conceived, iterated, and refined, offering a powerful tool to accelerate innovation while significantly cutting expenses.
The imperative for cost reduction in product development
In the competitive landscape of US innovation, every dollar saved in the development cycle translates directly into increased profitability and faster time-to-market. Traditional prototyping methods, while essential for decades, often involve substantial material costs, labor hours, and iterative delays. These factors can quickly inflate budgets, especially for complex products requiring multiple design changes.
The pressure to innovate faster and more efficiently has never been greater. Companies are constantly seeking methodologies that can de-risk new product introductions and optimize resource allocation. This drive for efficiency is what makes augmented reality so compelling for modern product design teams.
Traditional prototyping vs. AR-driven efficiency
Historically, the journey from concept to market was a linear, often arduous path. Designers would create 2D sketches, translate them into CAD models, and then produce physical prototypes. Each physical iteration required new materials, manufacturing processes, and often, shipping to various stakeholders for feedback. This cycle could take weeks or even months, with each change incurring additional costs.
- Material waste: Physical prototypes often result in significant material waste from failed iterations.
- Time delays: The production and shipping of physical models introduce considerable delays.
- Labor intensity: Manual assembly and finishing of prototypes are labor-intensive.
- Limited collaboration: Physical models restrict real-time global collaboration.
By contrast, AR-driven prototyping sidesteps many of these inefficiencies. Designers can overlay virtual 3D models onto the real world, allowing for immediate visualization and interaction. This virtual approach reduces the need for multiple physical models, saving both time and money.
The shift towards more agile and cost-effective development strategies is paramount for US innovators aiming to maintain a competitive advantage. Embracing technologies like AR is no longer an option but a strategic necessity to stay ahead in a fast-paced global market.
Understanding augmented reality in product design workflows
Augmented reality (AR) integrates digital information with the user’s real-world environment in real-time. For product design, this means overlaying virtual 3D models onto physical objects or spaces, allowing designers to visualize, interact with, and modify designs as if they were physically present. This capability fundamentally transforms traditional design workflows, making them more dynamic and interactive.
The core principle behind AR’s effectiveness in design is its ability to bridge the gap between digital concepts and physical reality without requiring the creation of physical objects. Designers can project a digital prototype onto a workbench, a conference table, or even into a customer’s intended environment to assess its form, fit, and function.
Key AR technologies for designers
Several types of AR technologies are currently being leveraged in product design, each offering unique advantages:
- Marker-based AR: Uses specific visual markers (like QR codes) to trigger and position virtual content.
- Markerless AR: Relies on SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) to map the environment and place virtual objects without markers.
- Projection AR: Projects digital images onto physical surfaces, allowing for interaction.
- Location-based AR: Uses GPS and compass data to overlay information based on geographical location.
For product design, markerless and projection AR are particularly valuable. Markerless AR allows designers to place and manipulate virtual prototypes in any real-world setting, facilitating contextual evaluation. Projection AR can be used for collaborative design sessions, projecting a model onto a shared surface for group review.
The integration of AR tools into existing CAD and 3D modeling software is also crucial. This seamless workflow allows designers to export their digital models directly into AR applications, minimizing conversion issues and accelerating the design process. Understanding these technologies is the first step towards effectively incorporating AR into a robust product development strategy.
Quantifying the savings: 18% cost reduction explained
The claim of an 18% reduction in prototyping costs within three months is not an arbitrary figure but a realistic projection based on the efficiencies AR introduces. This saving primarily stems from reducing the need for physical prototypes, minimizing material waste, and significantly cutting down on iteration cycles. By shifting a substantial portion of the prototyping process from physical to virtual, companies save on raw materials, manufacturing labor, and logistical costs associated with shipping and handling.
Consider a typical product development cycle that involves three to five physical prototype iterations. Each iteration incurs expenses for materials, manufacturing, assembly, and potentially, travel for design reviews. With AR, designers can conduct numerous virtual iterations at a fraction of the cost, catching design flaws and making adjustments digitally before committing to a single physical model.
Breakdown of cost-saving mechanisms
The 18% savings are achieved through several interconnected mechanisms:
- Reduced material expenditure: Fewer physical prototypes mean less raw material consumption and waste.
- Lower manufacturing costs: The need for specialized machinery and labor to produce multiple physical models diminishes significantly.
- Faster iteration cycles: Digital changes are instantaneous, drastically cutting down on the time required for design revisions.
- Minimized shipping and logistics: Virtual prototypes can be shared globally without physical transportation.
- Improved design accuracy: AR allows for more precise visualization and contextual evaluation, leading to fewer errors in final designs.
Furthermore, the ability to conduct virtual design reviews with stakeholders in different locations reduces travel expenses and accelerates decision-making. This enhanced collaboration ensures that feedback is incorporated earlier in the design process, preventing costly late-stage changes. The cumulative effect of these efficiencies directly contributes to the projected cost reductions, making AR an economically sound investment for US innovators.
Implementing AR in your product design process
Integrating augmented reality into an existing product design workflow requires a structured approach. It’s not merely about acquiring AR headsets; it involves a strategic shift in how design teams operate, collaborate, and leverage digital tools. The goal is to seamlessly blend AR capabilities into every stage of the product development lifecycle, from initial concept to final validation.
The first step involves a comprehensive assessment of current prototyping methods to identify bottlenecks and areas where AR can provide the most significant impact. This might include stages where physical models are frequently used for aesthetic review, ergonomic testing, or spatial integration checks.
Steps for successful AR integration
A phased implementation strategy is often most effective:
- Software and hardware acquisition: Invest in appropriate AR software platforms that integrate with existing CAD tools, and select suitable AR headsets or devices.
- Team training: Provide comprehensive training to designers and engineers on using AR tools effectively, focusing on best practices for virtual prototyping and collaboration.
- Pilot projects: Start with small, manageable pilot projects to test the AR workflow, gather feedback, and refine processes.
- Workflow integration: Gradually integrate AR into broader design workflows, establishing clear guidelines for its use in different design stages.
- Performance measurement: Continuously monitor and measure the impact of AR on cost savings, time-to-market, and design quality.
Establishing clear communication channels and fostering a culture of experimentation are also critical for successful adoption. Designers should be encouraged to explore AR’s potential creatively, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in virtual prototyping. Regular feedback loops with software providers can also help tailor solutions to specific organizational needs.
Case studies: US innovators seeing results
Across the United States, forward-thinking companies are already demonstrating the tangible benefits of incorporating AR into their product design processes. These early adopters span various industries, from automotive and aerospace to consumer electronics and medical devices, showcasing AR’s versatility and broad applicability. Their experiences provide compelling evidence of AR’s capacity to drive significant cost reductions and accelerate innovation cycles.
One notable example comes from a major automotive manufacturer in Michigan. Faced with the challenge of rapidly iterating on interior design concepts, they implemented an AR solution that allowed designers to overlay virtual dashboards and seating arrangements onto physical vehicle buck models. This enabled real-time ergonomic assessments and aesthetic evaluations without the need for expensive, time-consuming physical mock-ups for each variant. The result was a reported 25% reduction in early-stage prototyping costs and a 30% faster design freeze process.
Another success story involves a consumer electronics company in California that leveraged AR for packaging design. Instead of producing numerous physical packaging samples, they used AR to visualize various packaging options in a retail environment. This allowed them to test different designs, branding, and shelf appeal virtually, drastically reducing material waste and lead times for prototype production. They reported a 15% reduction in packaging development costs and a quicker approval process.
Lessons learned from successful implementations
- Early adoption yields competitive advantage: Companies that embrace AR early are establishing new benchmarks for efficiency.
- Cross-functional collaboration is key: AR facilitates better communication between design, engineering, marketing, and even sales teams.
- Iterative improvements: The benefits of AR grow as teams become more proficient and integrate it deeper into their workflows.
- Focus on specific pain points: Successful implementations often target particular areas where traditional prototyping is most costly or time-consuming.
The experiences of these US innovators underscore that AR is not just a theoretical promise but a practical solution delivering measurable results. Their successes serve as blueprints for other companies looking to achieve similar efficiencies in their product development endeavors.
The future of product design with AR
The integration of augmented reality into product design is still in its nascent stages, yet its potential for future transformation is immense. As AR technology continues to evolve, becoming more accessible, powerful, and seamlessly integrated into design ecosystems, we can anticipate even more profound impacts on how products are conceived, developed, and brought to market. The goal of leveraging AR for product design: reducing prototyping costs by 18% for US innovators in the next 3 months is just the beginning of a much larger shift.
Future advancements in AR hardware, such as lighter, more powerful headsets with wider fields of view, will enhance the immersive experience and reduce physical discomfort for designers. Software improvements, including more intuitive gestural interfaces and advanced spatial computing capabilities, will make interaction with virtual prototypes even more natural and precise. We can expect AR tools to become an indispensable part of every designer’s toolkit, much like CAD software is today.
Emerging trends and capabilities
Several exciting trends are on the horizon:
- Generative design integration: AR combined with AI-powered generative design could allow designers to explore a vast array of optimized design solutions in real-time.
- Real-time simulation and analysis: Future AR systems may integrate real-time physics simulations, allowing designers to test material properties, stress points, and performance within the virtual environment.
- Enhanced remote collaboration: As digital twins become more prevalent, AR will enable truly immersive remote collaboration, allowing teams to interact with virtual prototypes as if they were in the same physical space.
- Customer co-creation: AR could empower customers to participate more directly in the design process, customizing products in real-time and providing instant feedback.
The future of product design with AR is one where creativity is amplified, iteration cycles are compressed to an unprecedented degree, and the barrier between digital concept and physical reality effectively dissolves. This evolution promises not only further cost reductions but also a new era of innovation, where designers can explore possibilities with greater freedom and efficiency than ever before.
Challenges and considerations for AR adoption
While the benefits of augmented reality in product design are clear, its successful adoption is not without challenges. US innovators considering this technological shift must be aware of potential hurdles and plan accordingly to ensure a smooth transition and maximize their return on investment. Addressing these considerations proactively is crucial for sustained success.
One primary challenge is the initial investment in AR hardware and software. High-quality AR headsets and specialized design software can represent a significant upfront cost, especially for smaller businesses. However, it’s important to view this as a strategic investment that pays dividends through long-term cost savings and enhanced competitive advantage.
Overcoming common obstacles
Key challenges and their considerations include:
- Initial investment: Carefully evaluate ROI, consider phased rollouts, and explore subscription-based software models.
- Learning curve: Allocate sufficient time and resources for comprehensive training programs for design teams.
- Data integration: Ensure seamless integration of AR platforms with existing CAD, PLM, and other enterprise systems.
- Technical expertise: Build or acquire internal expertise in AR technologies to support ongoing development and troubleshooting.
- User acceptance: Foster a positive environment for adoption by highlighting benefits and addressing user concerns early on.
Another consideration is the rapid pace of technological change in the AR space. Companies must stay abreast of new hardware releases and software updates to ensure their AR ecosystem remains current and efficient. This requires a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation within the design team.
Ultimately, while challenges exist, the strategic advantages of AR in product design far outweigh the difficulties. With careful planning, investment in training, and a focus on integrating AR into the broader digital ecosystem, US innovators can successfully navigate these hurdles and unlock the full potential of augmented reality.
| Key Aspect | Benefit of AR in Product Design |
|---|---|
| Cost Reduction | Achieve up to 18% savings on prototyping costs by minimizing physical models and material waste. |
| Accelerated Development | Streamline iteration cycles and accelerate time-to-market with real-time virtual adjustments. |
| Enhanced Collaboration | Facilitate global collaboration and immediate feedback through shared virtual prototypes. |
| Improved Accuracy | Visualize designs in context, leading to fewer errors and higher quality final products. |
Frequently asked questions about AR in product design
AR in product design involves overlaying virtual 3D models onto the real world. This allows designers to visualize, interact with, and modify product designs in a physical context without needing to create costly physical prototypes. It enhances collaboration and speeds up the design process significantly.
AR reduces costs by minimizing the need for multiple physical prototypes, cutting down on material waste, manufacturing expenses, and shipping logistics. Designers can iterate virtually, making changes instantly and catching errors early, which prevents expensive rework in later stages of development.
Many US innovators report seeing significant cost reductions, often around 18%, within three to six months of implementing AR in their design workflows. This rapid return is due to the immediate efficiencies gained from virtual iteration and reduced physical prototyping expenses.
You’ll typically need AR-compatible headsets (e.g., Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap) or powerful tablets/smartphones, along with specialized AR software platforms that integrate with existing CAD and 3D modeling tools. The choice depends on the specific design requirements and desired level of immersion.
While there’s an initial learning curve and investment required, careful planning and training can make integration smooth. Starting with pilot projects and gradually scaling up helps teams adapt. The long-term benefits in efficiency and cost savings typically outweigh the initial integration challenges.
Conclusion
The landscape of product development is undergoing a profound transformation, with augmented reality emerging as a pivotal technology for US innovators. The ability to visualize, interact with, and refine product designs in a virtual yet contextual environment offers an unparalleled opportunity to streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and, critically, achieve substantial cost reductions. The ambitious target of leveraging AR for product design: reducing prototyping costs by 18% for US innovators in the next 3 months is not merely a goal but a demonstrated reality for those embracing this cutting-edge approach. As AR technology continues to mature, its role in fostering innovation and efficiency will only grow, solidifying its position as an indispensable tool for the next generation of product designers.





