Augmented Reality in US Healthcare: 3 FDA-Approved Apps for 2025
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing US healthcare with newly FDA-approved applications poised for widespread adoption by 2025, enhancing surgical precision, patient education, and rehabilitation through innovative visual overlays and interactive experiences.
The landscape of healthcare is rapidly evolving, and Augmented Reality in US Healthcare: 3 New FDA-Approved Applications for 2025 are set to be game-changers. As we look ahead, these applications promise to enhance patient care, improve surgical outcomes, and revolutionize medical training.
The Rise of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented Reality (AR) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day reality transforming various sectors, including healthcare. In the US, the adoption of AR technologies is gaining momentum, driven by the potential to improve patient outcomes, streamline workflows, and reduce healthcare costs. Understanding the fundamental role of AR sets the stage for exploring its specific applications and anticipated impact on healthcare.
AR differs from Virtual Reality (VR) in that it overlays digital information onto the real world rather than creating a completely immersive, artificial environment. This distinction makes AR particularly useful in healthcare settings, where real-time data and interaction with the physical environment are crucial. The ability to provide clinicians with immediate, context-aware information can significantly enhance decision-making and procedural accuracy.
Benefits of AR in Healthcare
- Enhanced Visualization: AR provides healthcare professionals with enhanced visualization of anatomical structures, allowing for more precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Improved Training: Medical students and residents can benefit from AR-based training simulations that offer realistic and interactive learning experiences.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: AR can be used to educate patients about their conditions and treatment options in an engaging and understandable manner.
- Streamlined Workflows: AR applications can help healthcare providers streamline workflows by providing real-time access to patient data and clinical guidelines.
The integration of AR in US healthcare is also supported by a growing body of research demonstrating its effectiveness and safety. As more healthcare providers recognize the benefits of AR and as the technology continues to mature, we can expect to see even wider adoption of this technology in the years to come.

FDA-Approved AR Applications: A New Era
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of AR applications marks a pivotal moment for the technology, signaling its safety and efficacy in healthcare settings. These approvals pave the way for broader adoption and integration of AR into clinical practice. Three recently FDA-approved AR applications stand out for their potential to revolutionize different aspects of healthcare.
These applications are not just innovative; they are also rigorously tested and evaluated to meet the FDA’s stringent standards. The FDA approval process ensures that these AR technologies are safe, effective, and reliable for use in diagnosing, treating, and managing various medical conditions. This validation is a crucial step in building trust and confidence among healthcare providers and patients.
Key Features of FDA-Approved AR Applications
- Data Integration: Seamless integration with electronic health records (EHRs) and other clinical data sources.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive and easy-to-use interface for healthcare professionals with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Real-Time Feedback: Provides real-time feedback and guidance to healthcare providers during procedures and patient interactions.
- Customizable Settings: Allows healthcare providers to customize settings and parameters to meet the unique needs of their patients and clinical settings.
As these FDA-approved AR applications become more widely available, they have the potential to transform healthcare delivery, making it more efficient, effective, and patient-centered. The impact of these technologies is expected to extend beyond clinical practice, influencing medical education, research, and healthcare policy.
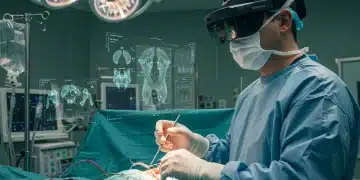
Application 1: AR-Enhanced Surgical Guidance
One of the most promising areas of AR application in healthcare is surgical guidance. AR-enhanced surgical tools provide surgeons with real-time, three-dimensional visualizations of anatomical structures, overlaid directly onto the surgical field. This technology can improve surgical precision, reduce the risk of complications, and shorten recovery times for patients.
AR-enhanced surgical guidance systems typically use advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to create detailed 3D models of the patient’s anatomy. These models are then registered to the patient’s body using sophisticated tracking systems, allowing surgeons to visualize internal structures in real-time during surgery.
Benefits in Surgical Procedures
The benefits of AR-enhanced surgical guidance extend to a wide range of surgical specialties, including:
- Neurosurgery: Precise localization of tumors and critical structures within the brain.
- Orthopedic Surgery: Accurate placement of implants and alignment of bones in joint replacement and fracture repair.
- Cardiovascular Surgery: Improved visualization of blood vessels and cardiac structures during bypass grafting and valve repair.
- ENT Surgery: Enhanced navigation through the complex anatomy of the ear, nose, and throat.
Clinical studies have shown that AR-enhanced surgical guidance can lead to significant improvements in surgical outcomes, including reduced operative time, decreased blood loss, and fewer complications. As the technology becomes more refined and affordable, it is likely to become a standard tool in surgical practices around the world.
Application 2: AR for Patient Education
Patient education is a critical component of healthcare, and AR offers innovative ways to engage and inform patients about their conditions and treatment options. By using AR to create interactive and immersive learning experiences, healthcare providers can empower patients to take a more active role in their own care.
AR-based patient education tools can take various forms, including:
- Anatomical Visualization: Patients can use AR apps to explore three-dimensional models of their own anatomy, gaining a better understanding of their condition.
- Treatment Simulations: AR can be used to simulate the effects of different treatments, helping patients make informed decisions about their care.
- Medication Reminders: AR apps can provide visual reminders to take medications, improving adherence and reducing the risk of missed doses.
By providing patients with clear and engaging information, AR can help reduce anxiety, improve adherence to treatment plans, and enhance overall patient satisfaction. As the technology becomes more accessible and user-friendly, we can expect to see more healthcare providers incorporating AR into their patient education programs.
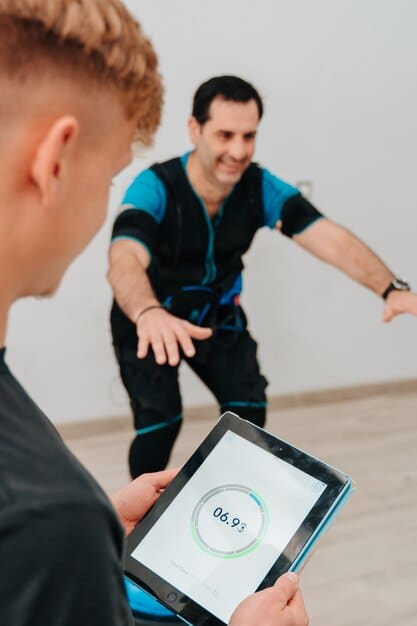
Application 3: AR in Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in helping patients recover from injuries, illnesses, and surgeries. AR offers innovative ways to enhance rehabilitation programs, providing patients with real-time feedback and guidance as they perform exercises and activities. This technology can improve patient motivation, promote faster recovery, and reduce the risk of re-injury.
AR-based rehabilitation systems typically use motion sensors and computer vision algorithms to track the patient’s movements and provide real-time feedback on their form and technique. Patients can use AR apps to perform exercises in a virtual environment, guided by virtual therapists or avatars.

Areas of Rehabilitation Where AR Can be Used
- Physical Therapy: AR can be used to guide patients through exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Occupational Therapy: AR can help patients relearn daily living skills, such as dressing, cooking, and writing.
- Speech Therapy: AR can be used to help patients improve their speech and language skills.
Studies have shown that AR-enhanced rehabilitation can lead to significant improvements in patient outcomes, including faster recovery times, increased adherence to therapy programs, and improved quality of life. As the technology becomes more sophisticated and affordable, it is likely to become an integral part of rehabilitation practices.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the potential of AR in healthcare is immense, there are also several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its successful adoption and integration. These challenges include:
- Cost: AR technology can be expensive, making it difficult for some healthcare providers to adopt.
- Training: Healthcare professionals need to be trained on how to use AR technology effectively.
- Data Security and Privacy: AR applications generate and collect large amounts of data, raising concerns about data security and privacy.
- Regulatory Framework: Clear regulatory guidelines are needed to ensure the safe and responsible use of AR in healthcare.
Despite these challenges, the future of AR in healthcare is bright. As the technology continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see even wider adoption and integration of AR into clinical practice. Future directions for AR in healthcare include:
- Personalized Medicine: Using AR to tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique genetic and clinical profiles.
- Remote Monitoring: AR-based remote monitoring systems can help healthcare providers track patients’ health status and provide timely interventions.
- Surgical Robotics: Combining AR with surgical robotics to enhance surgical precision and dexterity.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🩺 Surgical Guidance | Enhances precision with real-time 3D anatomical visualizations. |
| 📚 Patient Education | Provides interactive, immersive learning experiences for patients. |
| 💪 Rehabilitation | Offers real-time feedback during exercises, improving recovery. |
| 🔒 FDA Approval | Ensures safety and efficacy for clinical use in healthcare settings. |
FAQ
Augmented reality (AR) in healthcare involves overlaying digital information onto the real world, providing healthcare professionals and patients with enhanced visualizations, interactive experiences, and real-time data during medical procedures or treatments.
AR-enhanced surgical guidance improves surgical outcomes by providing surgeons with real-time, three-dimensional visualizations of anatomical structures, reducing operative time, decreasing blood loss, and minimizing the risk of complications.
AR supports patient education by offering interactive anatomical models, simulations of treatment effects, and medication reminders, leading to better understanding, adherence to treatment plans, and enhanced overall satisfaction among patients.
Limitations and challenges for AR in medicine include high technology costs, the need for specialized training, data security and privacy concerns, and the requirement for clear regulatory guidelines to govern its safe and responsible usage.
AR in the future healthcare will promote personalized medicine by tailoring care plans, enabling remote patient monitoring for timely interventions, and be combined with surgical robotics to improve surgical precision and effectiveness.
Conclusion
As Augmented Reality in US Healthcare: 3 New FDA-Approved Applications for 2025 become more integrated into various aspects of medicine, they hold the potential to transform the healthcare landscape. From enhancing surgical precision to improving patient engagement and revolutionizing rehabilitation, AR is poised to shape the future of healthcare delivery, making it more efficient, effective, and patient-centered.