Next-Gen Haptic Feedback Devices: 3 VR Innovations for 2025

The world of virtual reality is constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in digital immersion. By 2025, next-gen haptic feedback devices are set to redefine how we interact with virtual environments, moving beyond simple vibrations to deliver truly tactile experiences that blur the line between the digital and physical.
The Evolution of Haptic Feedback in VR
Haptic feedback, the technology that simulates the sense of touch, has long been a cornerstone of immersive experiences, from vibrating game controllers to smartphone alerts. However, its application in virtual reality has historically been limited, often relying on rudimentary vibration motors that provide a generalized sense of feedback rather than nuanced tactile sensations. As VR hardware advances, so too does the demand for haptic systems that can match the visual and auditory fidelity of virtual worlds.
The journey from simple rumble packs to sophisticated haptic devices is a testament to relentless innovation. Early VR haptics primarily focused on conveying impact or generic textures, often failing to replicate the subtle intricacies of physical interaction. This gap in sensory experience has been a significant barrier to achieving truly believable VR immersion. Developers and researchers have recognized this limitation, leading to a surge in investment and breakthroughs aimed at creating haptic technologies capable of delivering a far richer tactile palette.
Current Limitations and the Need for Innovation
Existing haptic solutions often suffer from a lack of fidelity and specificity. While they can communicate basic sensations like a crash or a buzz, they struggle with nuances such as the texture of a surface, the weight of an object, or the sensation of temperature. This creates a disconnect, reminding users that their virtual interactions are not quite real. The drive for innovation stems from the fundamental desire to overcome these limitations and unlock the full potential of VR.
- Limited tactile spectrum: Most devices offer only vibrotactile feedback.
- Lack of force feedback: Inability to simulate resistance or weight.
- Absence of thermal sensations: No replication of hot or cold.
- Bulky form factors: Devices can be cumbersome and restrict natural movement.
The need for more refined haptics is not just about enhancing gaming. It extends to professional applications like surgical training, product design, and remote collaboration, where precise tactile feedback can significantly improve learning outcomes and operational efficiency. The industry is actively seeking solutions that are both technically advanced and seamlessly integrated into the user experience.
Innovation 1: Advanced Vibrotactile Arrays and Micro-actuators
One of the most significant advancements in next-gen haptic feedback devices is the proliferation of advanced vibrotactile arrays and micro-actuators. Moving beyond simple eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors, these new technologies utilize sophisticated arrays of tiny, individually controllable actuators to generate highly localized and diverse tactile sensations. This allows for the simulation of intricate textures, precise impacts, and even the sensation of objects sliding across surfaces, drastically enhancing realism.
These arrays can be embedded into gloves, suits, and even standalone controllers, offering a granular level of control over the user’s sense of touch. Unlike older systems that produce a generalized vibration, micro-actuators can create distinct patterns across the skin, mimicking the feeling of different materials or the precise trajectory of a virtual projectile. This precision is crucial for experiences that demand high fidelity, such as handling virtual tools or interacting with delicate virtual objects.
The Power of High-Resolution Haptics
The concept of high-resolution haptics is centered around distributing numerous miniature actuators across a surface, each capable of independently modulating frequency and amplitude. This allows for the creation of complex haptic waveforms that can simulate a wide range of tactile phenomena. Imagine feeling the individual grains of sand, the slickness of ice, or the gentle rustle of leaves – all without physically touching them.
- Piezoelectric actuators: Offer fast response times and precise control.
- Electro-active polymers (EAPs): Provide flexible and conformable haptic surfaces.
- Microfluidic systems: Can create localized pressure and even subtle airflow.
The integration of these micro-actuators into flexible substrates is making haptic gloves and full-body suits lighter and less intrusive. This move towards more ergonomic designs ensures that the enhanced tactile feedback doesn’t come at the cost of comfort or freedom of movement. The goal is to make the haptic device feel like a natural extension of the user’s body, disappearing into the background as the virtual world takes center stage.
Innovation 2: Force Feedback Exoskeletons and Wearable Robotics
While vibrotactile feedback excels at simulating textures and vibrations, it falls short when it comes to replicating the physical resistance and weight of virtual objects. This is where force feedback exoskeletons and wearable robotics come into play, representing a monumental leap in next-gen haptic feedback devices. These sophisticated systems apply mechanical resistance to the user’s limbs, allowing them to feel the weight, stiffness, and impact of virtual objects as if they were physically present.
Imagine reaching out to grasp a virtual cup and feeling its solid weight, or pushing against a virtual wall and experiencing the unyielding resistance. These exoskeletons use motors and linkages to create physical constraints, preventing the user’s hand or arm from passing through a virtual object. This not only enhances immersion but also significantly improves the sense of presence and interactivity within VR environments, making interactions feel far more tangible and believable.
Beyond Handheld Controllers: Full-Body Immersion
Initial force feedback devices were often bulky and limited to specific parts of the body. However, advancements are leading to more compact, lightweight, and even full-body exoskeletons. These systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with VR headsets, providing a comprehensive haptic experience that extends beyond just the hands. The ability to feel resistance across the entire body opens up new avenues for training, gaming, and even rehabilitation.
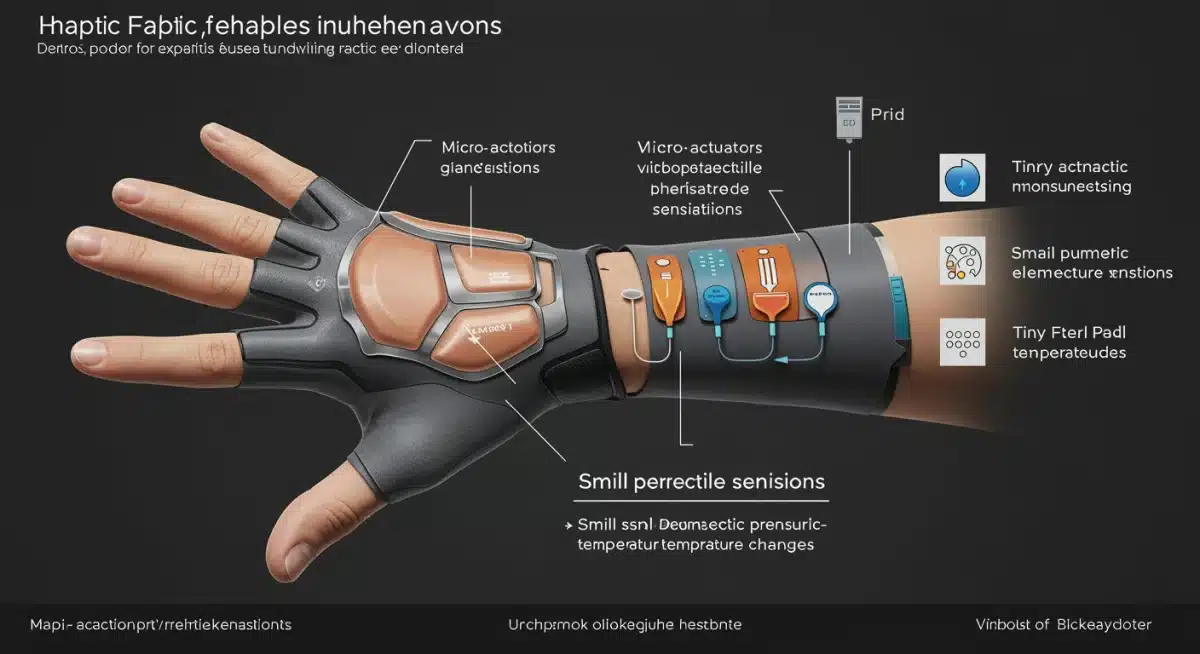
The development of these devices is not without its challenges, primarily concerning power efficiency, weight distribution, and safety. However, ongoing research is yielding promising results, with prototypes demonstrating remarkable capabilities. The future of VR will undoubtedly involve users not just seeing and hearing virtual worlds, but physically interacting with them in a way that feels utterly real, thanks to these innovative force feedback systems.
Innovation 3: Thermal and Electro-Haptic Feedback
Beyond mechanical resistance and vibrations, next-gen haptic feedback devices are exploring the frontiers of thermal and electro-haptic feedback to add another layer of sensory realism. Thermal haptics involves simulating temperature changes, allowing users to feel the warmth of a virtual fire, the chill of an icy surface, or the cool breeze in a digital landscape. This subtle yet powerful form of feedback can dramatically enhance environmental immersion and emotional connection within VR experiences.
Electro-haptic feedback, on the other hand, uses electrical impulses to stimulate nerve endings in the skin, creating a variety of sensations including pressure, texture, and even pain (at safe, controlled levels). While still in its nascent stages, this technology holds immense potential for delivering highly customizable and nuanced tactile experiences without the need for bulky mechanical components. It offers a pathway to truly subtle and pervasive haptic sensations.
Integrating Multisensory Feedback for Ultimate Realism
The true power of these innovations lies in their potential for integration. Combining advanced vibrotactile arrays with force feedback exoskeletons and thermal/electro-haptic elements creates a multisensory feedback loop that can trick the brain into believing virtual interactions are real. This holistic approach to haptics is what will ultimately define the next generation of VR immersion.
- Peltier elements: Commonly used for localized heating and cooling.
- Micro-heaters and coolers: Integrated into wearable fabrics for temperature simulation.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Adapted for localized haptic sensations.
Researchers are also exploring hybrid approaches, where different haptic modalities work in concert to create a more compelling illusion. For example, a virtual interaction might involve feeling the weight of an object (force feedback), its texture (vibrotactile), and its temperature (thermal haptics) all at once. This synergistic application of diverse haptic technologies is key to unlocking unprecedented levels of realism in virtual environments.
The Impact on Gaming and Entertainment
The implications of these next-gen haptic feedback devices for gaming and entertainment are profound. Imagine playing a VR game where you can physically feel every punch, every gust of wind, and the distinct texture of every weapon or surface. This level of immersion will transform passive consumption into active participation, making virtual worlds feel truly alive and responsive to your actions. Games will become more visceral, more engaging, and ultimately, more memorable.
Beyond traditional gaming, these advancements will open doors for new forms of interactive storytelling and entertainment. Virtual concerts could allow attendees to feel the vibrations of the music through their bodies, while interactive cinematic experiences could provide tactile cues that heighten emotional impact. The creative possibilities are virtually limitless, pushing the boundaries of what consumers expect from their entertainment.
New Genres and Experiences
The introduction of highly realistic haptic feedback could spawn entirely new genres of games and experiences. Escape rooms, horror games, and simulation titles would benefit immensely from the added layer of tactile realism, making scares more impactful, puzzles more tangible, and simulations more effective. Developers will have a richer palette of sensory tools to craft experiences that resonate deeply with players.
Furthermore, social VR platforms could integrate advanced haptics to allow for more meaningful virtual interactions, such as feeling a handshake or a high-five. This could bridge the physical distance between users and foster a greater sense of connection in virtual spaces. The goal is to move beyond mere visual and auditory presence to a full-bodied, authentic sense of being in a shared virtual environment.
Beyond Entertainment: Professional and Therapeutic Applications
While entertainment often drives innovation, the practical applications of next-gen haptic feedback devices extend far beyond gaming. In professional sectors, these technologies promise to revolutionize training, remote work, and even healthcare. Imagine surgeons practicing complex procedures on virtual patients, feeling the resistance of tissue and the texture of organs, all without risk. This level of fidelity can significantly reduce learning curves and improve proficiency.
For remote collaboration, haptic feedback could enable engineers to virtually manipulate prototypes, designers to feel fabric textures, or architects to explore structural integrity with tactile cues. This bridges the physical gap, allowing teams to work together on virtual objects as if they were in the same room. In therapy, haptics can aid in rehabilitation, providing sensory stimulation for patients recovering from injuries or neurological conditions, offering a new dimension to physical and occupational therapy.
Enhancing Training and Skill Development
Industries like aviation, manufacturing, and defense stand to gain enormously from advanced haptic training simulations. Pilots can feel the controls of a virtual aircraft, mechanics can simulate repairing complex machinery, and soldiers can train in realistic combat scenarios with tactile feedback for weapons and environments. This hands-on, immersive training can lead to faster skill acquisition and higher retention rates, ultimately improving safety and performance in real-world operations.
Moreover, for individuals with sensory impairments, haptic technology could open new avenues for interaction and perception. For example, haptic wearables could convert visual or auditory information into tactile patterns, providing alternative sensory input. This potential for inclusivity underscores the transformative power of these emerging technologies, making VR not just more immersive, but also more accessible and beneficial to a wider population.
Challenges and the Path Forward
Despite the exciting advancements, the development and widespread adoption of next-gen haptic feedback devices face several challenges. Cost remains a significant barrier, as sophisticated haptic systems are currently expensive to produce and integrate. Miniaturization, power efficiency, and ergonomic design are also ongoing research areas, as devices need to be lightweight, comfortable, and capable of long operational times without frequent recharging.
Another crucial aspect is the standardization of haptic feedback protocols. For widespread compatibility and ease of development, there needs to be a common language for how haptic sensations are encoded and transmitted across different devices and platforms. Without this, developers will face fragmentation, limiting the reach and impact of their haptic-enhanced experiences. Addressing these challenges is paramount for the future success of immersive VR.
The Role of Research and Collaboration
Overcoming these hurdles requires continued investment in research and strong collaboration across industries. Academic institutions, technology companies, and even government agencies are working together to push the boundaries of haptic science. This collaborative effort is crucial for developing new materials, improving actuator technologies, and creating more intuitive and efficient algorithms for haptic rendering.
Furthermore, user experience research will play a vital role in refining these devices. Understanding how different haptic sensations are perceived and interpreted by users is essential for creating truly compelling and effective feedback. As these challenges are systematically addressed, the path forward for next-gen haptic devices looks increasingly promising, paving the way for a future where virtual reality is indistinguishable from physical reality.
| Key Innovation | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Advanced Vibrotactile Arrays | Utilize micro-actuators for localized, high-resolution tactile sensations, simulating textures and precise impacts. |
| Force Feedback Exoskeletons | Apply mechanical resistance to limbs, allowing users to feel the weight, stiffness, and impact of virtual objects. |
| Thermal and Electro-Haptics | Simulate temperature changes (hot/cold) and create diverse sensations via electrical impulses on the skin. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Next-Gen Haptics
The primary goals are to enhance VR immersion by providing more realistic and nuanced tactile sensations, going beyond simple vibrations. This includes simulating textures, weight, temperature, and localized pressure to make virtual interactions feel more tangible and believable for users.
Unlike older systems that often used single, generalized vibration motors, advanced vibrotactile arrays employ numerous tiny, individually controlled actuators. This allows for highly localized and diverse tactile feedback, enabling the simulation of intricate textures and precise impacts across the skin, greatly increasing fidelity.
Force feedback exoskeletons enable users to feel the physical resistance, weight, and stiffness of virtual objects. This means you can feel a virtual sword’s weight, push against a solid virtual wall, or grasp an object and feel its form, significantly enhancing the sense of presence and physical interaction.
Yes, thermal haptics is a key innovation. Devices can integrate elements like Peltier modules to simulate hot or cold sensations, allowing users to feel the warmth of a virtual fire, the chill of ice, or even the subtle temperature shifts in a virtual environment, adding a new layer of sensory realism.
Key challenges include high manufacturing costs, the need for further miniaturization and power efficiency to ensure comfort and practicality, and the development of standardized haptic feedback protocols. Addressing these will be crucial for making these advanced technologies accessible to a broader consumer market.
Conclusion
The landscape of virtual reality is on the cusp of a profound transformation, driven by the rapid advancements in next-gen haptic feedback devices. The integration of advanced vibrotactile arrays, force feedback exoskeletons, and thermal and electro-haptic feedback is moving VR beyond mere visual and auditory immersion towards a truly multisensory experience. By 2025, these innovations promise to deliver unprecedented levels of realism, making virtual worlds not just seen and heard, but fully felt. This evolution will not only revolutionize entertainment but also unlock significant potential across professional training, therapeutic applications, and remote collaboration, fundamentally reshaping how we interact with digital environments.





